How Were The Tectonic Plates Formed?
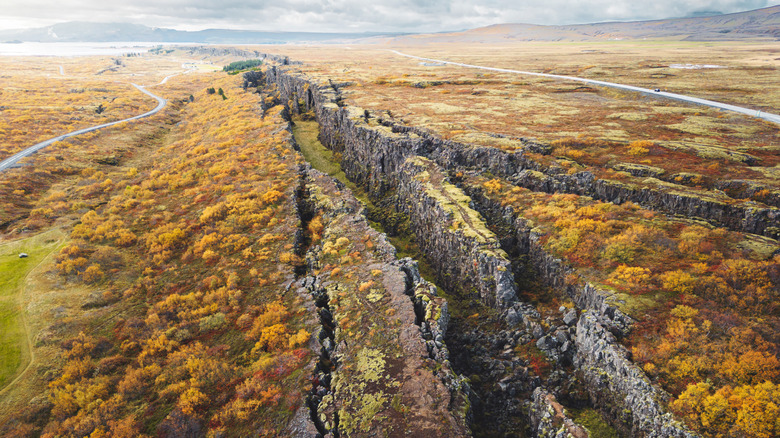
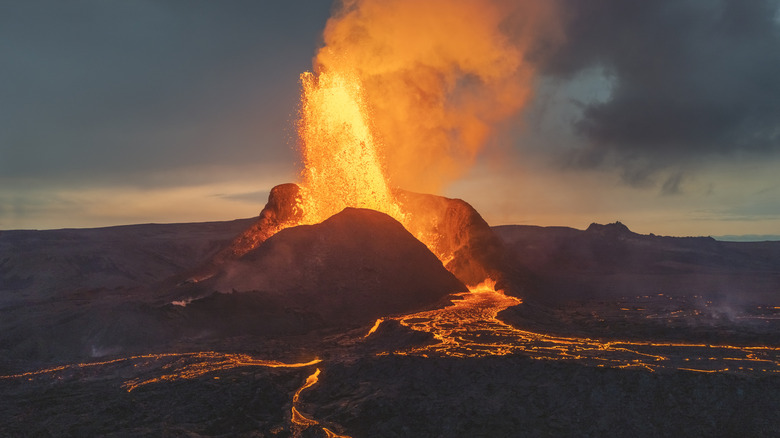
The tectonic plates are among the most powerful forces on Earth, exerting tremendous influence over every single life that unfolds on this planet. They are both creators and destroyers, capable of raising whole mountain ranges and leveling cities with earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. At this very moment, tectonic plates are in the process of ripping Africa apart, a transformation that will completely reshape the world. Yet for all their importance, scientists don't actually know how the tectonic plates came to be.
Not only is there no consensus as to the origins of the tectonic plates, but scientists can't even agree on when they formed. Some argue that plate tectonics were in action as long as 4 billion years ago, making them almost as old as the planet itself. Other geologists would push back on this, insisting that the plates are a mere 1 billion years old. The answer is likely somewhere in between, but this is only the tip of the iceberg.
As for how tectonic plates came to be, several theories have emerged over the years. One school of thought is that the plates formed as the planet's crust first began to cool, though once again, there is controversy over exactly how those boundaries formed where they did. More recently, novel theories have emerged, including the bold idea that Earth's crust may have once been one piece that later shattered from internal pressure. But all this uncertainty is frustrating, and it raises the question, why can't scientists figure this out?
A timeline of the tectonic plates
In order to figure out how the tectonic plates originally formed, it's necessary to find out when they first formed. That issue alone has ignited significant debate within the scientific community that goes back as far as the theory of tectonics itself. Some argue that the plates are 4 billion years old while others argue that they only formed around 1 billion years ago.
Determining a timeline was immensely challenging, as only the most ancient rocks on Earth date back far enough to find answers. However, the 2010s brought some degree of clarity to the issue. Studies in Greenland and Australia found evidence of rock layers moving beginning around 3.2 billion years ago. That would mean that the tectonic plates didn't form until Earth was already over a billion years old, but while it helps to narrow down the timeline, the question of how the plates formed at all remains a controversy.
Theories behind tectonic plate formation
Several theories have emerged to explain the origins of the tectonic plates. A long-running theory posits that for the first billion years of Earth's existence, the crust was still forming as Earth cooled, but then the core began to cool and the crust hardened. Some researchers argue that the plates formed at this point due to density differences within the newly solidified crust causing it to break into pieces.
Some have argued that the tectonic plates formed through essentially the same processes they undergo now. As the planet's crust solidified, parts of it cooled faster than others, and got pulled downward while hotter parts of the crust rose up, a process that continues to this day. As you read this, North America is slowly sinking due to these very forces.
In 2020, a different theory was put forth, and may be the most convincing yet. A research team of American and Chinese scientists created a computer model to reenact the planet's infancy. In a paper published in Nature Communications, they present evidence for the expanding Earth hypothesis. This hypothesis argues that Earth's crust originally cooled into one piece, but by doing so, it trapped what heat was still radiating from the core. This heat eventually built up so much that the planet began to expand, fracturing the surface to accommodate its swelling. This model is still quite new, but hopefully, it may finally bring some closure to one of geology's biggest mysteries.