NASA Launches New Mission With SpaceX To Map Space Weather
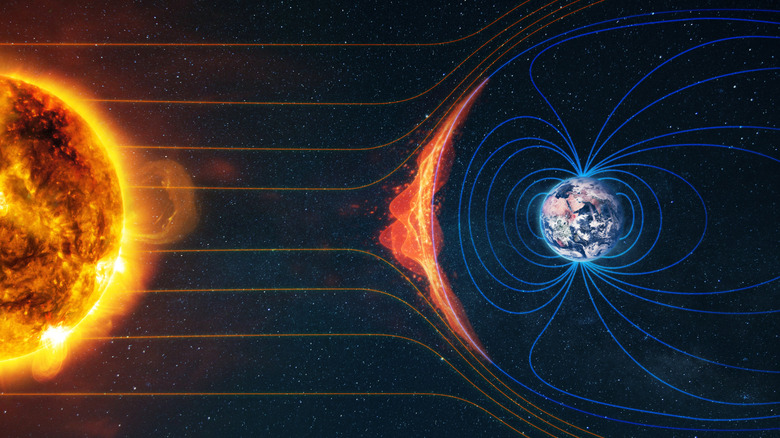
The NASA Space Weather Program studies how weather in space affects not only humans on Earth, but also how it could create challenges for astronauts and spacecraft on missions. Space weather is a term that refers to the way the sun impacts us and other objects in our solar system. Things like solar wind, solar flares, and particle events can influence our GPS signals, power grids, and even create atmospheric drag on flying crafts. As we know from research on old trees, solar storms can pose a catastrophic threat to our society.
NASA aims to study space weather in order to forecast it accurately. In the same way you might alter your plans if you knew a thunderstorm was approaching, NASA wants to be able to predict space weather events more accurately to guide our reactions to them. It will be helpful not only for Earth operations but also for missions in space, where astronauts are particularly vulnerable.
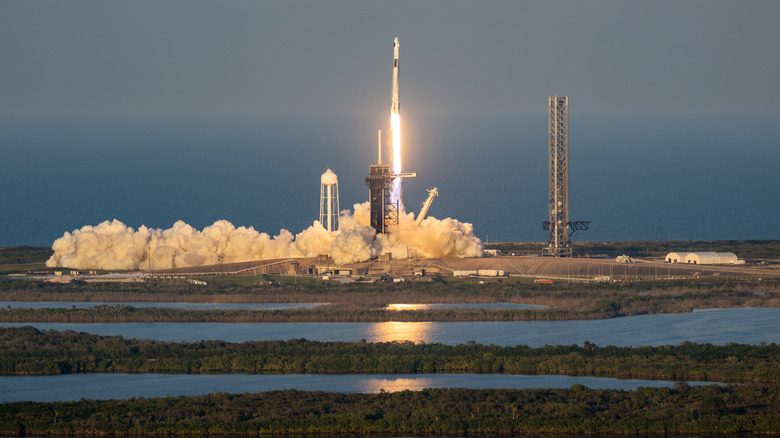
A collaboration is underway between NASA, SpaceX, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). On September 24, 2025, a rocket launch carried critical equipment to study space weather. This three-part mission will lay the foundation for a future where we can better understand and forecast the weather outside of Earth.
What has been launched for this space weather mission
The SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket carried three mission crafts. One was the Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe. Known as IMAP, it will study the boundaries of the heliosphere, examining how Earth is protected from galactic cosmic rays due to solar wind activity, the source of which we may have recently discovered. IMAP will be charting this region and taking solar wind and energetic particle samples for research into potential dangers.
The Carruthers Geocorona Observatory craft launched alongside the mapping probe. It has a landmark mission focusing on exploring the exosphere. Its purpose is to record and analyze exosphere changes, such as the impact of solar storms on it. This will enhance our understanding of the way solar activity affects our daily lives on Earth.
The final craft launched was the Space Weather Follow On-Lagrange 1 spacecraft, or SWFO-L1. This belongs to NOAA. It will be a space-based weather observatory. It will function much like the radars and observation towers that local weather stations use. The SWFO-L1 will monitor space weather in real-time and report changes. It can alert NASA of potential dangers or other weather activities we need to be aware of and adjust to.
The details of this new mission and its future
Currently, these three craft are en route to their mission sites. All are functioning well and are expected to be at their destinations by January 2026. Not only is this an exciting collaboration among NASA, SpaceX, and NOAA, but it will also provide us with critical space weather information. This mission establishes future processes to monitor events occurring outside our planet, such as the largest solar flare observed since 2017.
This mission brings together a global effort. David McComas of Princeton University and 27 global partner organizations helm the IMAP program. Lara Waldrop of the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign is leading the Carruthers Geocorona Observatory mission alongside the Space Sciences Laboratory at the University of California, Berkeley. The Goddard Space Flight Center is also lending its expertise to both missions, while NOAA is taking responsibility for its SWFO-L1.
Associate administrator for the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington, Dr. Nicola Fox, issued a statement on NASA's website, "As the United States prepares to send humans back to the Moon and onward to Mars, NASA and NOAA are providing the ultimate interplanetary survival guide to support humanity's epic journey along the way." She also said that, "Our scientific discoveries and technical innovations directly feed into our know-before-you-go roadmap to ensure a prepared, safe, and sustained human presence on other worlds."