4 Big Changes Coming To NASA In 2026
In 2026, NASA will move from long-running development and testing into a phase defined by action, readiness, and progress. After years shaped by delays, redesigns, and risk reductions, many of NASA's most ambitious programs are finally lining up for execution. The result will be a year that could redefine how humans explore space and how science missions are delivered. Human spaceflight is once again the central focus.
After more than 50 years, humans are planning to return to the Moon. At the same time, the agency is testing new ways to communicate across deep space, manage crews, and operate complex systems from Earth. Meanwhile, the next-generation Nancy Grace Roman telescope is finished and preparing to launch, while NASA continues to build strong partnerships with commercial companies to improve its means to search for life outside Earth. Together, these efforts make 2026 more than just another year of planning. It represents a moment when planning turns into progress.
Artemis II is going back to the Moon
In 2026, NASA plans to take a major step in returning humans to the Moon with the Artemis II mission. This flight will be the first time astronauts reach the moon since the final Apollo mission concluded in 1972. A crew of four astronauts aboard NASA's Orion spacecraft will leave Earth from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The mission is planned to launch no later than April 2026, but NASA is actually aiming for a possible launch even sooner.
The trip will last only 10 days, during which the spacecraft will loop around the Moon and return to Earth. The astronauts won't land on the Moon because the true purpose of the Artemis II mission is to test life support, navigation, communication, and other systems with humans aboard in a deep-space environment. That said, Artemis II is more than just a technical tryout. It's a confidence builder for the later Artemis missions planned to take astronauts to the lunar surface, Mars' surface, and beyond. The excitement for Artemis II is global. NASA invited the public to sign up and have their names fly around the Moon during the mission. Projects like this can help people around the world feel more connected to space exploration in 2026.
NASA hones in on search-for-life missions
In early January 2026, NASA announced that it was hearing proposals from companies who could help advance technology on the successor to James Webb, the Habitable Worlds Observatory (HWO). NASA plans to have HWO serve as a space telescope designed to image Earth-like planets orbiting distant suns and analyze their atmospheres for signatures of life. This new flagship telescope will push beyond what Hubble and James Webb can do. While these existing telescopes also have coronagraphs, or devices that block starlight so that scientists can get a better look at orbiting planets, HWO is expected to have one that is thousands of times more powerful.
NASA awarded three-year contracts to seven companies to build the technical foundations for HWO. Among these are some major players including Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, and BAE Systems. In a statement, NASA administrator Jared Isaacman said humanity is ready to find life beyond Earth and that he believes developing such technology is a matter of urgency. HWO is NASA's boldest step yet in answering the question: Are we alone in the universe?
Laser-based communication is implemented
In recent years, NASA has been pushing the limits of how space communication works. Until now, spacecraft were using traditional radio waves to communicate with Earth. Now, new technologies are laser-based. They use pulses of light to send information, packing far more data in each transmission. This breakthrough could transform how missions share high-definition images, video, and scientific data across millions of kilometers.
NASA already successfully demonstrated how Deep Space Optical Communication (DSOC) works. The Psyche spacecraft, launched in October 2023, is equipped with this new technology, and it already received laser-encoded data over record-breaking distances. The first stream was, funnily enough, a video of a cat chasing a laser pointer. Throughout 2024 and 2025, the DSOC onboard Psyche continued to beat distance records.
This successful demonstration lays the groundwork for the operational use of laser communication in crew-supported missions like Artemis II. NASA will fly the Orion Artemis II Optical Communication System (O2O) aboard the Orion spacecraft. The Artemis crew will be able to send 4K ultra-high definition video, voice, procedures, images, and science data for the duration of the mission.
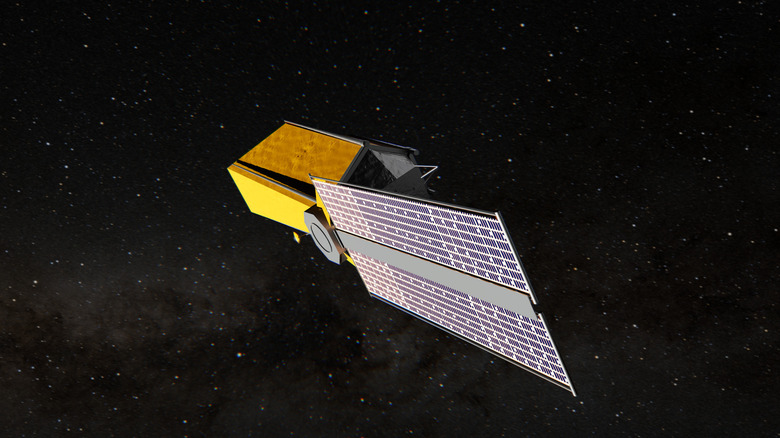
The Nancy Grace Roman telescope finishes its final tests
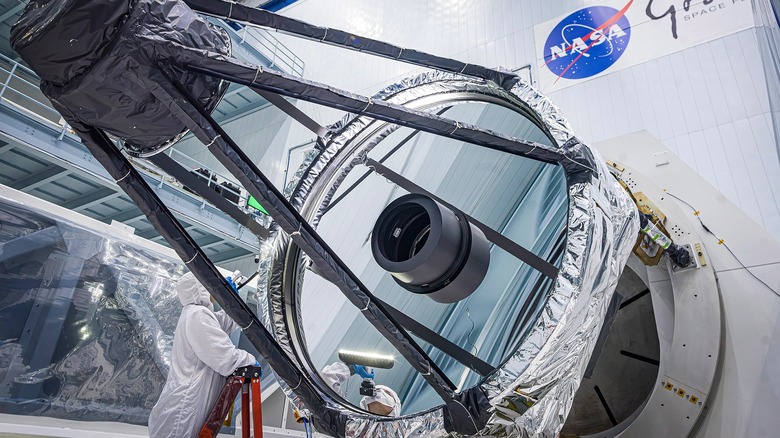
NASA's next great space telescope, the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope has officially moved from construction to completion. After years of development, the spacecraft's physical build is finished, and all major components have been assembled and integrated. Roman is NASA's next flagship telescope that combines Hubble-like resolution with a field view 100 times larger. That means it's capable of capturing huge cosmic areas in a single image.
The next step is to launch this space telescope. Final testing and preparations are ongoing as engineers simulate the launch vibrations, cold of space, and long-term operations far from Earth to make sure this next-generation telescope will be fully operational before the launch. The telescope is scheduled to go online in May 2027, but as the work progresses fast, there are indications that the launch could be moved to September 2026. While the launch preparations continue, the scientific community is already gearing up. In 2025, NASA called for research proposals using the Ronan telescope. It could be that 2026 sees some of these come to life.